Tropical Forest Canopy Height: Climate Change Insights
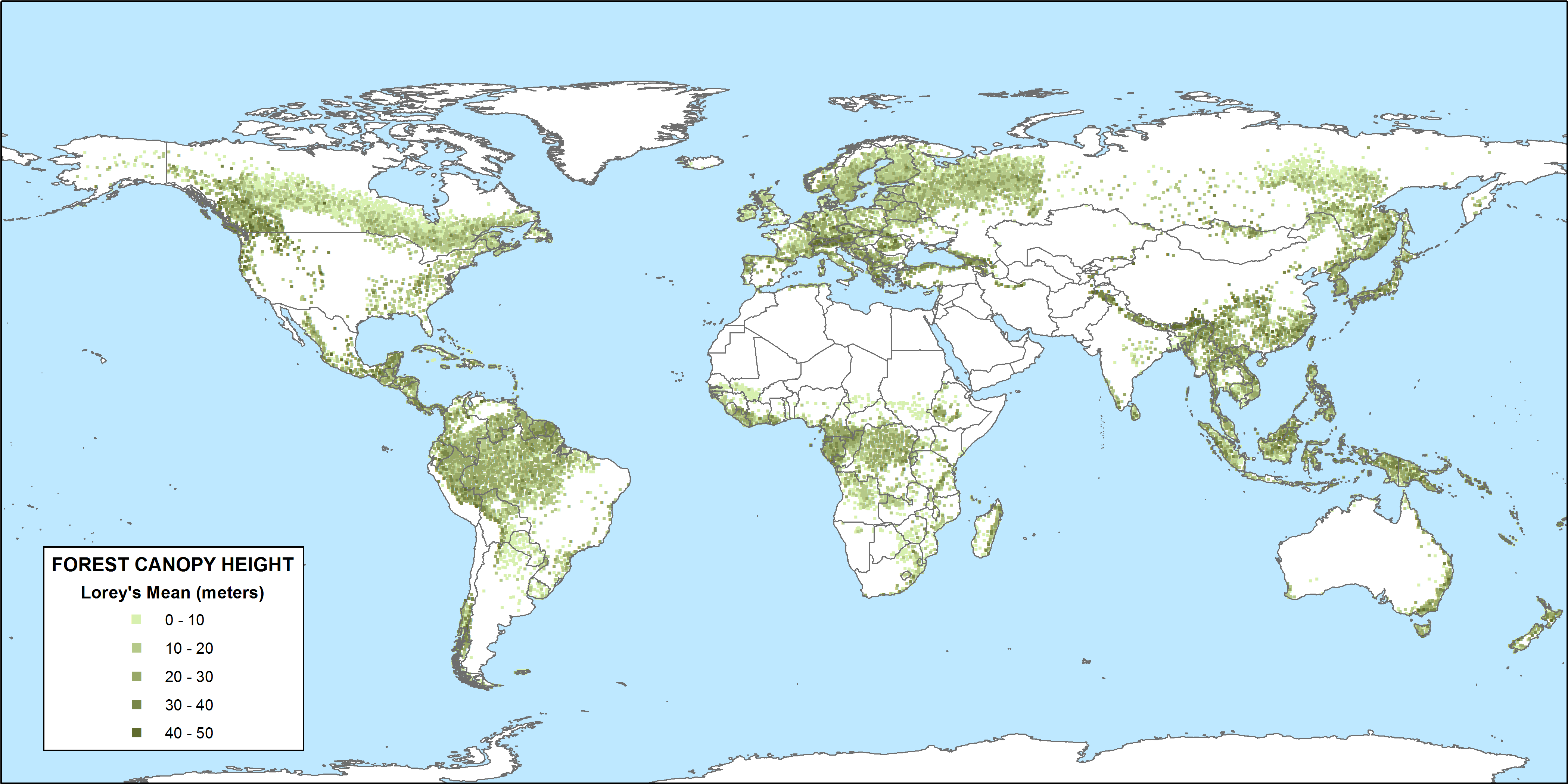
Tropical forest canopy height is a crucial metric for understanding the health of these biodiverse ecosystems and their role in carbon storage. Recent advancements by NASA, particularly through the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI), have enhanced our ability to assess how climate change impacts these towering layers of foliage. By employing advanced LiDAR technology from the International Space Station, researchers have gained unprecedented insights into the variations in canopy heights across tropical regions. Not only do taller canopies typically indicate greater ecosystem productivity, but they also serve as vital forest health indicators when analyzing the consequences of global warming. This understanding is essential for tropical forest conservation efforts, as policymakers seek to mitigate climate change and protect these vital ‘lungs of the Earth.’
The height of tropical forest canopies, often referred to as the upper tree layer, is an important measure of ecosystem vitality and resilience. In the quest for accurate assessments of forest conditions, scientists have turned to NASA’s GEDI technology, which utilizes laser-based measurements to determine where climate change is influencing these forests the most. By exploring different regions worldwide, researchers are able to gather data that illustrates how climatic factors like drought and temperature fluctuations affect canopy structure. Ultimately, this knowledge is pivotal for developing strategies aimed at conserving tropical forests, which play a significant role in carbon absorption and overall ecological health. As we delve deeper into this topic, the insights gained will prove indispensable for safeguarding these essential environments against the ongoing threat of climate change.
The Importance of Tropical Forest Canopy Height
Tropical forest canopy height serves as a vital indicator of forest health and ecosystem productivity. It plays a significant role in carbon storage, which is essential for combating climate change. Taller canopies are generally associated with abundant above-ground biomass. As such, they contribute to better microclimate regulation, helping to ameliorate extreme weather conditions such as heat waves. This makes understanding canopy height a priority for ecologists and conservationists alike, given its direct relationship to both biodiversity and climate moderation.
Research utilizing NASA’s GEDI technology has demonstrated that forest canopy height can fluctuate significantly due to various environmental factors, including temperature and precipitation patterns. For instance, in the study focused on the southern Amazon, the prolonged dry seasons attributed to climate change were found to severely impact canopy height. As global climate models predict even longer dry periods, the implications for carbon storage capacity and forest health are profound, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive monitoring and conservation efforts.
NASA GEDI: A Tool for Assessing Forest Health
NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) represents a groundbreaking advancement in satellite technology used for monitoring the Earth’s forests. By employing LiDAR laser instruments aboard the International Space Station, GEDI enables scientists to capture detailed measurements of forest structure, including canopy height and leaf density. This capability allows for more extensive coverage than previous methods, facilitating a broader understanding of how regional climatic conditions impact forest ecosystems, particularly in tropical regions.
The wealth of data produced by GEDI is invaluable for assessing forest health indicators. These insights are crucial as scientists strive to understand the relationship between climate variables like soil properties, topography, and seasonal climatic changes affecting forest profiles. As evidenced in recent studies, the GEDI findings are shaping conservation strategies by highlighting vulnerable tropical forests that require urgent protection to sustain their role in carbon sequestration and biodiversity.
Climate Change Impact on Tropical Forests
The repercussions of climate change on tropical forest ecosystems are becoming increasingly evident, especially regarding canopy height dynamics. As illustrated in recent studies, alterations in precipitation patterns and prolonged dry seasons are reshaping the structure of tropical forests, particularly in areas like the southern Amazon. Such changes present a dual challenge: not only do they threaten biodiversity, but they also compromise the forests’ ability to serve as carbon sinks.
The effects of climate change are not uniform across different regions, raising the need for targeted conservation policies. The GEDI studies reveal that factors such as elevation play a significant role in determining how climate change impacts canopy height, particularly in more humid environments like the central Amazon. As awareness of these discrepancies increases, it is essential for policymakers to leverage this knowledge to prioritize forested areas most at risk.
The Role of Forest Conservation in Mitigating Climate Change
Conserving tropical forests is paramount to mitigating climate change effects. These forests are often referred to as “Earth’s lungs” due to their remarkable capacity for carbon storage. Protecting these ecosystems not only preserves biodiversity but also maintains the critical services these forests provide, such as climate regulation and soil preservation. As evidence mounts regarding the detrimental impacts of climate change on canopy height and overall forest health, the urgency of conservation efforts grows.
Developing strategies to safeguard tropical forests can also support local communities that depend on these resources for their livelihoods. By integrating conservation with sustainable economic practices, it becomes possible to address both ecological and socio-economic challenges. Leveraging data insights from NASA’s GEDI can lead to effective policies that conserve forest habitats while promoting resilience against climate variability.
Understanding the Drivers of Canopy Height Variability
Investigating the underlying factors that influence tropical forest canopy height is crucial for forest management and conservation strategies. The recent research indicates that climatic variables, including solar radiation and precipitation patterns, account for a significant proportion of the variations in canopy height across different geographical contexts. Understanding these drivers enables scientists and policymakers to predict how forests may respond to ongoing climate changes.
Moreover, the exploration of canopy height variabilities aids in identifying specific areas that are critically vulnerable to climatic shifts. For example, researchers found that canopy heights in the southern Amazon were significantly affected by prolonged dry seasons, emphasizing the need for targeted conservation efforts in these regions. By enhancing our knowledge of these essential dynamics, conservation initiatives can be better tailored to maintain forest health and support carbon sequestration processes.
Implications for Global Climate Policy and Action
The insights derived from studies on tropical forest canopy height have far-reaching implications for global climate policy. As evidence mounts on how these forests impact carbon storage and overall ecosystem health, it becomes increasingly clear that they play an integral role in addressing climate change. A comprehensive understanding of their vulnerabilities allows policymakers to develop strategies that prioritize forest conservation as a means of mitigating climate-related risks.
Moreover, incorporating scientific findings into policy debates can drive international collaboration towards protecting these vital ecosystems. As climate change continues to threaten diverse habitats globally, the necessity for immediate and effective action becomes more pronounced. By harnessing research tools such as NASA’s GEDI, stakeholders can make informed decisions that foster the long-term integrity of tropical forests and their invaluable contributions to carbon management.
Technological Advances in Forest Monitoring
With advancements in technology, particularly NASA’s GEDI, the ability to monitor tropical forest health has reached unprecedented levels. The LiDAR technology enables researchers to visualize forest canopy structures and assess their condition with remarkable accuracy. Such tools are essential for understanding how environmental factors influence forest resilience and carbon storage capabilities.
As monitoring technology continues to evolve, it opens new avenues for research and conservation strategies. Real-time data from GEDI can facilitate quicker responses to ecological threats, such as deforestation or habitat degradation. By equipping forest scientists with the ability to track changes dynamically, we improve our capacity to protect tropical forests and ensure they continue to function as crucial carbon sinks amidst global climate challenges.
The Interconnectedness of Climate Change and Biodiversity
The relationship between climate change impacts and biodiversity is a critical aspect of tropical forest ecosystems. Many species rely on stable canopy heights and forest structures for their habitats and survival. Disruption from climate variability threatens not just the trees but also the myriad of life forms that depend on these environments, illustrating the interconnected nature of ecological systems.
Recognizing the importance of biodiversity in maintaining forest health highlights the need for integrated conservation efforts. By fostering policies that promote biodiversity alongside carbon storage initiatives, we can develop more effective strategies against climate change. Such approaches may also enhance ecosystem resilience, allowing forest regions to better withstand environmental stressors.
Future Research Directions in Tropical Forest Studies
The future of tropical forest research is poised for growth, particularly in light of recent advancements introduced by NASA’s GEDI program. Researchers are eager to expand their focus beyond isolated forest stands to encompass broader regional scales. By understanding varying canopy height dynamics across a diverse array of tropical forests, scientists can glean insights critical to climate change adaptation.
Future studies will likely emphasize the interplay between environmental variables, ecological integrity, and forest management practices. As our understanding deepens, the foundation will be laid for more nuanced conservation strategies that cater to regional biodiversity needs and climate resilience. Ultimately, ongoing research will be essential in informing effective policy decisions and fostering sustainable practices that ensure the longevity of these vital ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of tropical forest canopy height in relation to climate change?
Tropical forest canopy height is a crucial indicator of forest health and ecosystem productivity, as highlighted by NASA’s GEDI technology. Taller canopies generally indicate higher carbon storage and greater above-ground biomass, making them vital for mitigating climate change. Changes in canopy height due to climate change can impact carbon sequestration and the overall health of tropical forests.
How does NASA’s GEDI technology measure tropical forest canopy height?
NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) employs LiDAR laser technology aboard the International Space Station to measure tropical forest canopy height globally. GEDI’s measurements provide valuable insights into the vertical structure of forests, helping researchers understand how climate change factors like heat and drought impact these critical ecosystems.
What impact does climate change have on the height of tropical forest canopies?
Climate change significantly affects tropical forest canopy height by altering precipitation patterns, increasing dry seasons, and affecting overall environmental conditions. For instance, studies show that longer dry seasons can lead to reductions in canopy height, particularly in vulnerable areas like the southern Amazon, which are essential for carbon storage and biodiversity.
Why are taller tropical forest canopies important for forest health?
Taller tropical forest canopies are associated with higher carbon storage and greater biodiversity. They help regulate local microclimates, reducing temperatures during heat waves and supporting various species. Research indicates that they play a critical role in assessing the health of tropical forests and their ability to respond to climate change.
What role does elevation play in determining tropical forest canopy height?
Elevation is a significant factor influencing tropical forest canopy height. In regions like the central Amazon, elevation affects moisture availability and climatic conditions, which in turn impacts canopy height. NASA’s GEDI findings show that varying elevation levels account for differences in forest structure and health, emphasizing the need for targeted conservation efforts.
How can understanding tropical forest canopy height inform conservation efforts?
Understanding the environmental factors influencing tropical forest canopy height is essential for effective conservation strategies. By identifying areas vulnerable to climate change and assessing their carbon storage capacity, policymakers can prioritize conservation efforts to protect these critical ecosystems, using insights from NASA’s GEDI data.
What are the implications of reduced tropical forest canopy height for carbon storage?
Reduced tropical forest canopy height directly impacts carbon storage capacity, as shorter canopies generally correlate with decreased biomass and carbon sequestration potential. As climate change continues to influence canopy height, it may compromise the forests’ ability to function as effective carbon sinks, worsening the effects of climate change globally.
What measures can be taken to protect tropical forests from climate change?
Protecting tropical forests from climate change involves implementing conservation policies based on scientific research, such as studies utilizing NASA’s GEDI data. Strategies include reducing deforestation, restoring degraded forest areas, and prioritizing conservation efforts in regions identified as vulnerable to climate impacts to ensure they can continue to store carbon and support biodiversity.
| Key Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Tropical Forest Canopy Height | Crucial indicator of forest health and ecosystem productivity, influenced by climate, topography, and soil properties. |
| NASA’s GEDI Technology | Uses LiDAR from the International Space Station to measure canopy height variations across tropical forests. |
| Environmental Factors | Climate change, particularly heat and drought, significantly impacts canopy height. |
| Vulnerability of Canopies | Southern Amazon faces risks from prolonged dry seasons affecting canopy height. |
| Importance for Policy | Understanding canopy height is crucial for carbon sequestration, conservation, and climate change policies. |
Summary
Tropical forest canopy height is a vital measure reflecting the health of these ecosystems and their ability to act as carbon sinks. Recent studies leveraging NASA’s GEDI technology have highlighted the significant impact of climate change on canopy height variations across global tropical forests. As key indicators of forest productivity, understanding these dynamics is essential for further conservation efforts and climate change mitigation strategies.